Water ecological restoration and construction
Summary: Even after controlling external pollution, water bodies still face challenges from internal pollution (such as nutrient release from sediments, sediment resuspension, etc.) and ecosystem imbalance (such as the loss of key species and the disruption of trophic cascades), which can easily lead to repeated water quality problems and ecological degradation. Based on niche theory and steady-state transition mechanisms, our company creates oxygen-rich habitats, introduces aquatic vegetation, benthic animals, and indigenous fish, reconstructs the food web structure, restores biodiversity, achieves a dynamic balance of "producers + consumers + decomposers", enhances the system's self-purification capacity and ecological resilience, and ensures the long-term stability and sustainability of water bodies.

Introduction to River and Lake Ecological Restoration Plan (Aquatic plants and animals + ultra-nano gas dissolved oxygen system)
A complete aquatic ecosystem should include aquatic plants, aquatic animals, microorganisms, and their natural habitats.
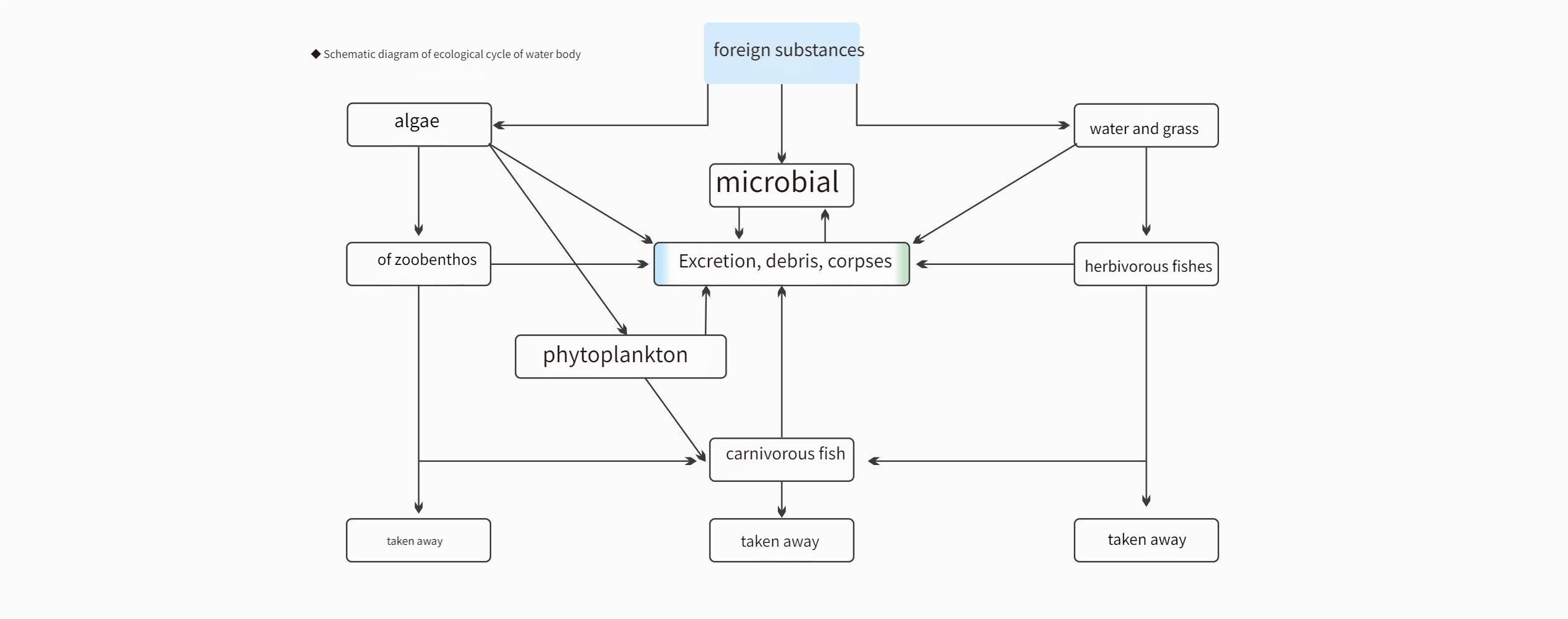
▼Diagram of aquatic ecosystem circulation
Aquatic plant regulation technology
Common submerged plants used in aquatic ecological restoration include: Vallisneria spiralis, Potamogeton crispus, Myriophyllum spicatum, Hydrilla verticillata, Najas minor, Ceratophyllum demersum, Potamogeton pectinatus, etc.
Aquatic animal regulation technology
Aquatic animals generally include benthic animals, fish, and zooplankton.
Fish are at the highest level of the aquatic food chain. In the water body, algae serve as food for plankton, which in turn serves as food for fish, forming a food chain: bacteria → algae → plankton → fish.
Utilizing the food chain relationship for effective resource recovery and utilization, achieving comprehensive benefits such as water purification, resource utilization, and ecological effects.
▼Diagram of aquatic animal ecological niche





